a
AT BEST HEALTHCARE IN PRISON IS ‘BASIC,’ IT WILL BE MUCH DIFFERENT THAT YOU’RE USED TO.
a
Prison Policy Initiative noted in a February 2025, Report,
“Correctional healthcare” differs from traditional healthcare as it prioritizes the needs of correctional facilities over those of incarcerated individuals. It operates more as a cost control system aimed at limiting expenses and avoiding lawsuits rather than genuinely caring for health. In this model, prisons are the primary customers, sidelining the health needs of the people within them.
a
WHAT A COMPREHENSIVE PREPARATION OF YOUR MEDICAL FILE LOOKS LIKE
- DIAGNOSTIC TESTS: CT, MRI, PET, EEG, EEG, NUCLEAR, BLOOD LABS; All with their reports, along with their CD or Flash Drives
- ALL DOCTORS RECORDS: SURGICAL, PATHOLOGY, REPORTS, PHYSICIAN CONTACT INFORMATION, MEDICATIONS ( AND IF THEY ARE ON FORMULARY, NON-FORMULARY, OR JUST NOT AVAILABLE), THEN A PLAN OF WHAT TO DO IF THEY ARE NOT AVAILABLE OR ON THE NON-FORMULARY LIST.
THE FEDERAL BUREAU OF PRISONS HAS SOME JUDGES BELIEVING THAT THEY ARE EQUIPPED TO PROVIDE THE CARE THAT YOU NEED.
a
WHAT YOU DO NOT WANT IS TO FIND YOURSELF IN A PRECARIOUS SITUATION.
a
1. THANKFULLY THERE ARE JUDGES LIKE FEDERAL JUDGE JESSE M. FURMAN WHO KNEW THIS NOT TO BE TRUE, AND IN A RECENT CASE, QUOTED THIS TEXT See, e.g., Sent’g Tr. at 19-21, United States v. Days, No. 19-CR-619 (CM) (S.D.N.Y. Apr. 29, 2021), ECF No. 35
a
2. FEDERAL Judge Roy Dalton Holds Federal Bureau of Prisons in Contempt.
- FCI Seagoville, a low-security federal correctional facility where Bardell is housed, has been the hardest hit federal prison in the nation by COVID-19
- October 10, 2022, Judge Holds Federal Bureau of Prisons in Contempt for Allowing Man To Waste Away From Untreated Cancer.

a
Another example of the importance of a 1) Comprehensive Presentence Report, and 2) Understanding the Administrative Remedy Process, and 3)How loved ones can assist your efforts from home.
a
MEDICAL HEALTHCARE VIDEOS
This video provides an overview of how healthcare is provided in federal prisons and is dependent on several factors. First, an accurate and comprehensive Presentation Report, and then, unfortunately, staffing, due to a severe shortage at that time. As of 9/2024, shortages continue.
As of 10/2023, a client returned from Butner Low and reported that only contracted doctors would come in from the outside to the Low and FMC (the BOP’s best hospital) every 2-3 weeks. All surgeries were going to Duke Medical Center, which is good. This is just something to keep in mind as, hopefully, things there have improved.
a
a
Through my story, this video explains why finding the right attorney for you is essential. Although this is your life-altering event, preparation and Knowledge of what you are about to do could still result in a positive outcome. Knowing that the DOJ has a 98% conviction rate, what is a positive outcome for you? Learn from my experiences through my video.
G
a

MINT Programs
a
IF YOU ARE NOT SURE WHAT TO DO FIRST, START WITH A FREE CONSULTATION FOR YOU OR A LOVED ONE. THIS IS MY PERSONAL CELL (240.888.7778), AND I ANSWER AND RETURN ALL CALLS.
We are not Attorneys; you need Legal Representation.
a
Corrections Agencies’ Responses to Opioid Abuse in Facilities (CIC, 2017)
a
NEW Reentry Act legislation is introduced that expands access to health care, including mental health services and substance use disorder treatment, for Medicaid-eligible individuals 30 days before their release from jail or prison.
Senators Tammy Baldwin (D-WI) and Mike Braun (R-IN), 3/30/2023
a
Before any initial designation decision is made, DSCC staff assess a provisional BOP CARE LEVEL from I–IV for each inmate. BOP institutions also have a care level assignment that reflects the medical care resources available at that facility.

The Designation and Sentencing Computation Center (DSCC) designates those inmates with Medical (and Mental Healthcare) CARE LEVEL I and II.
The Office of Medical Determinations and Transportation (OMDT) will make the designation decision for inmates with medical (and mental healthcare) care levels III and IV.
Co-published, The Critical Role of the Presentence Report. In this video I have added commentary that I hope you find helpful.
L
a
Prisoners have a constitutional right to adequate medical care, but what that means and how to get needed treatment is often not well understood by attorneys representing criminal defendants. This article attempts to address that knowledge deficit by explaining the medical, mental health, and substance abuse programs and policies within the federal Bureau of Prisons (BOP), as well as some educational, vocational, and other available programs intended to rehabilitate inmates and prepare them for return to society.
Equally important, the article explains the Critical Role of the Presentence Report (PSR) in determining whether and how treatment and programs will be available to a defendant. Documentation is paramount, and the diligent attorney must proactively gather and supply the appropriate documentation to the probation officer preparing their client’s PSR. In this video, I read the article published in The Federal Lawyer on Medical Care in Federal Prisons, with commentary throughout. If you have a medical issue, I recommend listening; it is very informative and detailed.
a
MEDICATIONS: AVAILABLE ON THREE TIERS [PSR DOCUMENTED]
- ON-FORMULARY: WHEN VERIFIED IN THE PSR, THE ODDS ARE BETTER YOU WILL GET THEM
- NON-FORMULARY: NOT IN PSR – NOT AVAILABLE,
- NON-FORMULARY: AND DOCUMENTED IN PSR STILL MAY NOT AVAILABLE, BUT THE ODDS ARE BETTER THROUGH THE ADMINISTRATIVE REMEDY
- NOT AVAILABLE, SIMILAR TO NON-FORMULARY: MAKE A PLAN THAT INCLUDES YOUR PHYSICIAN, ATTORNEY, AND SOMEONE WITH BOP KNOWLEDGE.
a
MEDICAL CO-PAYS:
Inmate Copayment Program P6031.02
Published in the Bureau of Justice Statistics,’ The findings are clear: medical copays in prisons are associated with worse access to healthcare behind bars.
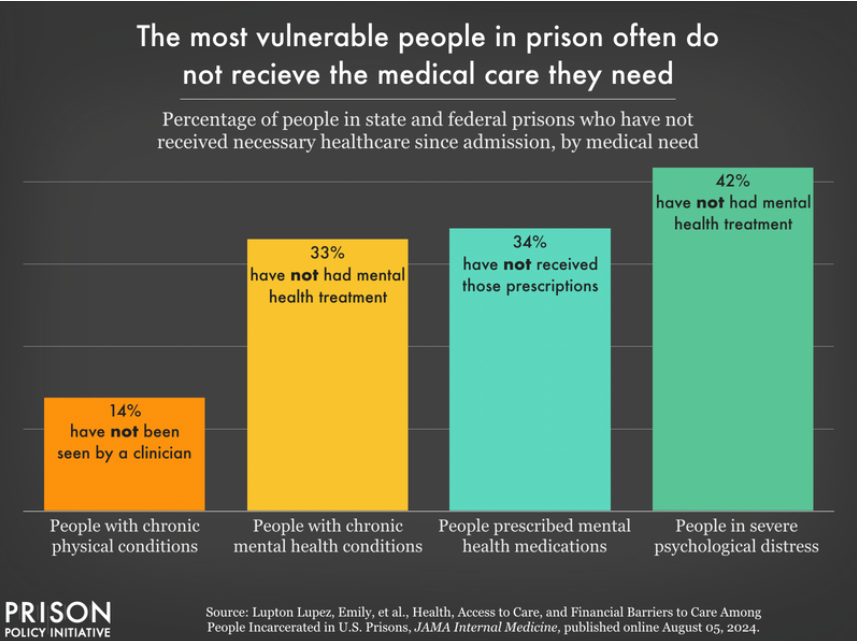
a
MEDICAL HEALTHCARE IS DELIVERED THROUGH CARE LEVELS
Medical Health CARE LEVEL I
- Inmates are generally healthy but may have limited medical needs that can be easily managed by clinician evaluations every six months.
- Inmates are less than 70 years of age.
- Examples: mild asthma or diet-controlled diabetes that do not require medications.
- Community Hospital Medical centers may be located over one hour away.
Medical Health CARE LEVEL II (the majority of BOP facilities)
- Inmates are stable outpatients who require at least quarterly clinician evaluations.
- It can be managed in chronic care clinics, including mental health issues.
- Examples: medication-controlled diabetes, epilepsy, and emphysema.
- Hospital Medical centers may be located within one hour of the facility.
Medical Health CARE LEVEL III
- Inmates are fragile outpatients who require frequent clinical contact to prevent hospitalization.
- They may require some assistance with activities of daily living (BOP Program Statement 5200.05, page 2), but do not need daily nursing care.
- Examples: cancer in remission for less than one year, advanced HIV disease, severe mental illness in remission on medication, severe congestive heart failure, and end-stage liver disease.
- The designation is done by the BOP’s Office of Medical Determinations and Transportation (OMDT).
Medical Health CARE LEVEL IV
- Functioning is severely impaired.
- Cannot perform Activities of Daily Living (ADL), such as caring for oneself, performing manual tasks, eating, sleeping, walking, standing, sitting, reaching, lifting, bending, speaking, breathing, learning, reading, concentrating, thinking, communicating, bathing, and cleaning oneself.
- Requires 24-hour skilled nursing care or nursing assistance.
- Examples: cancer on active treatment, dialysis, quadriplegia, stroke or head injury patients, major surgical patients, acute psychiatric illness requiring inpatient treatment, and high-risk pregnancy.
- BOP’s OMDT does the designation.
- Federal Medical Centers.
- FMC Butner (North Carolina), the BOP’s cancer center, provides inpatient medical/surgery, mental healthcare, and sex offender treatment programs, as well as housing at all security levels.
- FMC Carswell (Texas) is the only facility just for women.
- FMC Devens (Massachusetts) provides dialysis, one of several facilities that provide a residential sex offender program, along with inpatient mental healthcare.
Inspection of the BOP’s Federal Medical Center Devens, 2024
E
- FMC Fort Worth (Texas)
- FMC Lexington (Kentucky) houses lower security.
- FMC Rochester (Minnesota); contracted with the Mayo Clinic, providing all levels of complex medical care and inpatient mental healthcare.
- FMC, Springfield (Missouri); higher security, dialysis, and inpatient mental healthcare.
BOP Psychology Programs
Medication availability (~ 3500 different drugs) falls into 3 tiers
a
- Available- On Formulary (Which are they?)
- Non-Formulary; Requires a lengthy Preauthorization Process. Which are they? How do you ensure their availability to your client from day 1 of admission?
- Just not available; what similar (equivalent) substitutions will be used? Now, what can you do if this impacts Continuity of Care and is not within the Standard of Care in the Medical Community?
BOP COVID-19 Modified Operational Level Indicators [9/2024, Not in operation]
The challenge is that although the Pandemic is now behind us (10/2023), as an Epidemic, it will remain since the COVID virus continues to mutate. This has researchers around the world busy, along with the residual effect that persists in some POST-COVID Long-Haulers. It is significant that POST-COVID Long-Haulers may test negative but are very symptomatic. In turn, they may be unable to participate in ADL or PADL.
BOP General Modifications For Testing, Masks, Vaccines, and Boosters;
The BOP does not appear to conduct random COVID Testing proactively, nor do they keep accurate records (requiring?) of all Vaccines and Boosters given (to staff and inmates), nor do they enforce (or at least make available) Masks. We now know that vaccine immunity decreases over time (as in < Months). Compassionate Release or Second Look may be an option if you are immunocompromised.
Learn CPR – Save Lives – Hands-Only (30 sec) – The Next Life It Saves Could Be Yours.
“As a cardiologist, I have been frustrated learning of athletes dying on the playing field unnecessarily, and resuscitating people brought into our ER with no brain viability, because people do not know what to do, and it’s so simple. We have to change this.”
— DR. HOLLY S. ANDERSEN


